面试问题
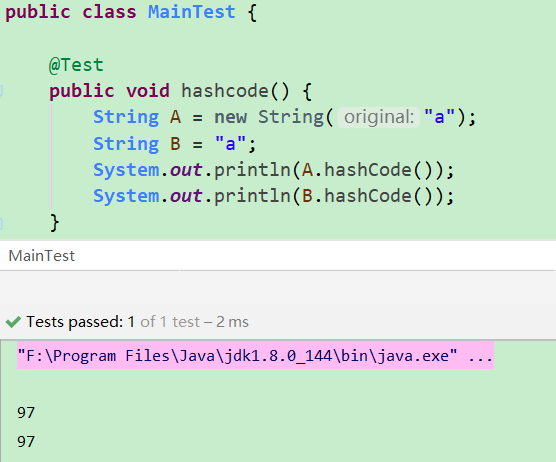
1 | String A = new String("a"); |
A,B 是否相等,如果都往HashSet里面放,会是什么结果?
答案:
A==B的判断为false;A.equals(B)为true;- 往 HashSet 里面放时,A 和 B 会当做一个相同的元素。因为往 HashSet 中 add 时,实际上是往一个 HashMap 中 put 元素,key 为 add 的元素,value 是一个固定值,而 HashMap 做 put 操作时判断 key 是否相等是这样判断的:
e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))。A 和 B 的 hashcode 方法得到的结果是一样的,所以A==B或者A.equals(B)有一个为true即会当作同一个key。
引申问题:==与equals()的区别?
==:对于引用类型比较的是地址值是否相同。equals:对于引用类型,默认是和==一样,即比较的是地址值是否相同。但如果类重写了equals方法,比如 String ,则是根据重写后的equals方法具体内容来判断。
String类的equals方法其实就是先通过==判断,如果结果为false,再根据对象指向的具体字符串,将字符串转成字符数组之后一个一个比较数组的元素是否完全相同。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36/**
* Compares this string to the specified object. The result is {@code
* true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null} and is a {@code
* String} object that represents the same sequence of characters as this
* object.
*
* @param anObject
* The object to compare this {@code String} against
*
* @return {@code true} if the given object represents a {@code String}
* equivalent to this string, {@code false} otherwise
*
* @see #compareTo(String)
* @see #equalsIgnoreCase(String)
*/
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
原理分析
String A = "ABC"内存会去查找永久代(常量池) ,如果没有的话,在永久代中中开辟一块儿内存空间,把地址付给栈指针,如果已经有了”ABC”的内存,直接把地址赋给栈指针。
因此
String str1="aa";
Srting str2="aa";
String Str3="aa";
……
这样下去,str1==Str2==str3;会一直相等下去。==的判断和equals()的判断都相等,因为他们的地址都相等,因此只在常量池中有一份内存空间,地址全部相同。
而String str = new String("a")是根据”a”这个String对象再次构造一个String对象;在堆中从新new一块儿内存,把指针赋给栈,
将新构造出来的String对象的引用赋给str。 因此只要是new String(),则栈中的地址都是指向最新的new出来的堆中的地址。这样==是判断地址的,当然不相同;而至于equals,因为是根据String类型重写后的equals()方法,其结果会是true。
下面是画图分析: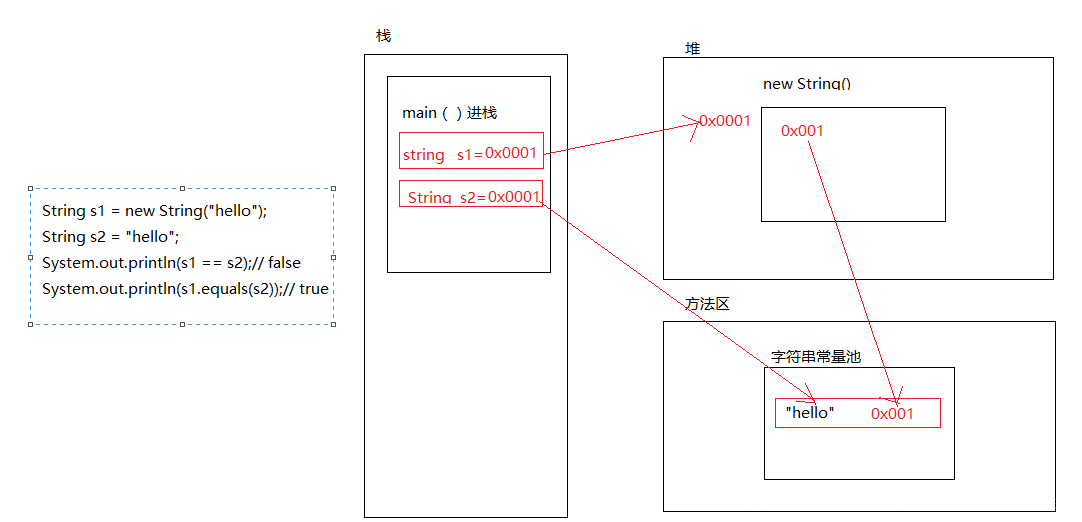
另外需要注意,如果两个字符串对象使用连接符+连接,将会生成一个新的字符串对象。即在堆中会开辟一个空间,并在栈中用一个引用类型指向这个地址。
代码演示
1 |
|