引言
当我们的服务部署在多个节点上时,为了防止重复提交请求,在下单、退款等业务处理中都需要借助分布式锁来保证业务逻辑的正确性。在分布式锁—简单的redis分布式锁一文中借助redis我们简单地实现了分布式锁的功能,但如果想要成熟的方案,Redis官方推荐的Redisson是更好的选择。本文主要介绍一下redisson分布式锁的原理与使用。
示例
本文示例基于Spring Boot 2的maven多模块项目。
maven依赖
引入redisson-spring-boot-starter依赖,其他的在此省略。1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- redisson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.11.5</version>
</dependency>
redis配置
在application.yml文件中配置redis的信息,配置方式和springboot整合redis时配置的方式一样。
单个redis节点的配置
1
2
3
4
5spring:
redis:
host: 172.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: 123456redis集群的配置方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10spring:
redis:
cluster:
nodes:
- 192.168.10.1:6379
- 192.168.10.2:6379
- 192.168.10.3:6379
- 192.168.10.4:6379
- 192.168.10.5:6380
password: 123456
代码
- 启动类
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson; |
- redis锁的工具类
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson.lock; |
- 订单业务service类
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson.service; |
- 另外两个辅助类
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson.enums; |
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson.thread; |
- 单元测试类
1 | package com.lzumetal.springboot.redisson.test; |
单元测试运行结果
在上面的单元测试中,模拟了同时对一个订单发起退款请求,运行的结果日志如下,可以看到最终订单只被退款了一次。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
302020-08-06 20:37:15.586 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.586 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单退款成功|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.600 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.605 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.606 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.611 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.613 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.613 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.618 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.619 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.620 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.622 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.625 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.626 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.628 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.628 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-2] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.628 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-2] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.635 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-1] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.635 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-1] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.635 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-2] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.639 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-1] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.639 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.640 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.645 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-5] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.647 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.648 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.649 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-4] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.653 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : lock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345,waitSeconds=10s|true
2020-08-06 20:37:15.653 WARN 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.service.OrderService : 订单已退款|orderId=12345
2020-08-06 20:37:15.655 INFO 15544 --- [pool-1-thread-3] c.l.s.redisson.lock.RedissonLockUtil : unlock|END|key=LOCK_ORDER_REFUND:12345
redisson锁的实现机制
原理示意图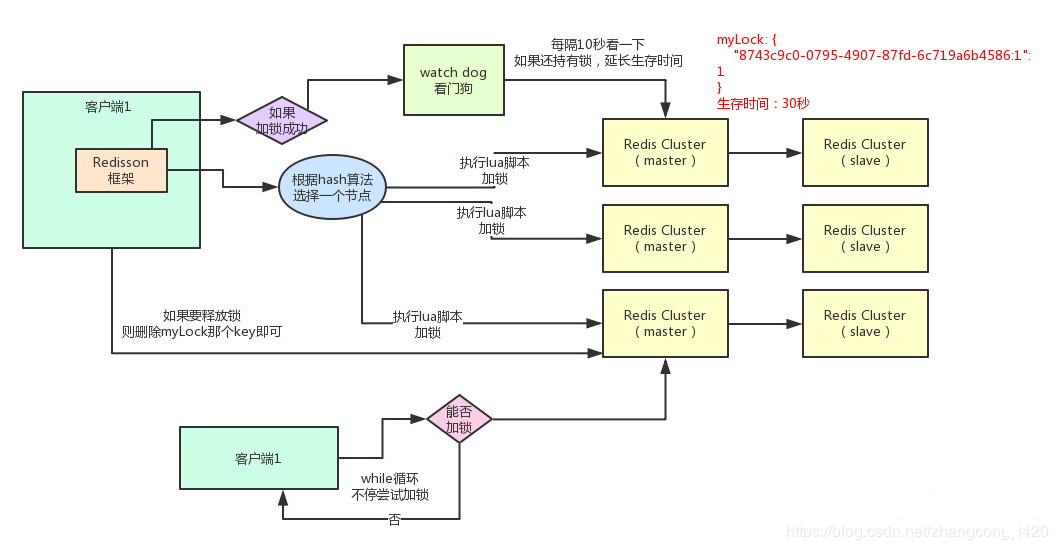
Redis Eval 命令
Redisson锁的实现是依靠大量的EVAL命令,EVAL命令可以使用lua解析器执行lua脚本。
EVAL命令的基本语法如下:1
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL script numkeys key [key ...] arg [arg ...]
参数说明:
- script: 参数是一段 Lua 脚本程序。
- numkeys: 用于指定键名参数key的个数。
numkeys可以区分key数组和arg数组,例如2 a b c ,假设numkeys是2,说明前2个参数 a 和b是key,第三个参数c是arg;1 a b c ,假设numkeys是1,说明前1个参数 a 是key,第2个参数起都是arg。 - key [key …]: 表示在脚本中所用到的那些 Redis 键(key),这些键名参数可以在 Lua 中通过全局变量 KEYS 数组,用 1 为基址的形式访问( KEYS[1] , KEYS[2] ,以此类推)。
- arg [arg …]: 附加参数,在 Lua 中通过全局变量 ARGV 数组访问,访问的形式和 KEYS 变量类似( ARGV[1] 、 ARGV[2] ,诸如此类)。
lua脚本中调用redis命令
Lua脚本中调用redis命令可以使用2个函数,如下:
- redis.call()
- redis.pcall()
redis.call()与redis.pcall()相似,二者唯一不同之处在于如果执行的redis命令执行失败,redis.call()将产生一个Lua error,从而迫使EVAL命令返回一个错误给命令的调用者,然而redis.pcall()将会捕捉这个错误,并返回代表这个错误的Lua表。
redis.call()和redis.pcall()命令参数是一个格式化后的redis命令,如下:1
2 eval "return redis.call('set','foo','bar')" 0
OK
上述eval命令执行脚本:设置key=foo,对应value=bar,但是它违背了EVAL命令的语法,因为Lua脚本中使用所有的键都应当使用KEYS数组动态赋值,上述脚本调整如下:1
2> eval "return redis.call('set',KEYS[1],'bar')" 1 foo
OK
加锁机制
如上图所示,当某个客户端需要加锁,如果当前系统使用的redis是一个集群,首先会根据hash节点选择一台机器(注意,仅仅只是选择一台机器!这点很关键!),然后执行源码中的这段lua脚本: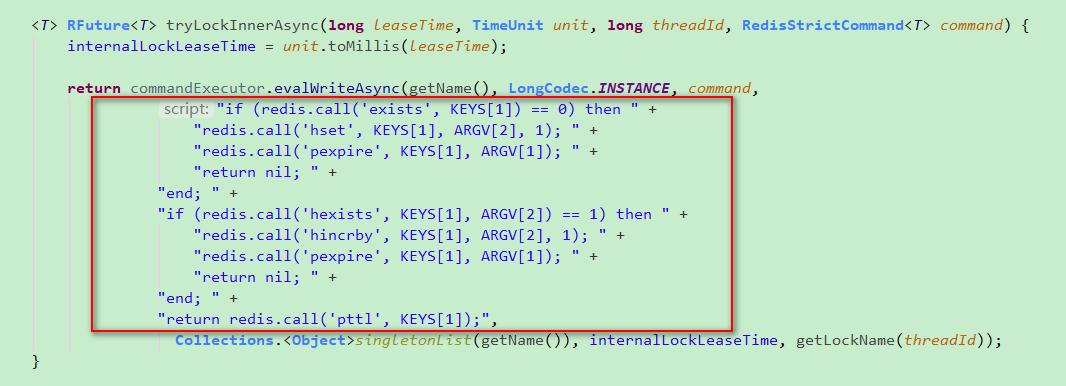
分析一下这段lua脚本:
命令中的字段
KEYS[1]表示的是加锁的那个在redis中的key,比如RLock lock = redisson.getLock(“myLock”);,key就是“myLock”。
ARGV[1]表示key的过期时间,默认是30s。
ARGV[2]代表的是加锁的客户端的ID,类似于这样:8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1锁不存在的情况下加锁
第一个判断语句,就是先用exists命令判断一下key是否存在,如果不存在则加锁。这个加锁过程也分为两步(但这两步是原子性的):执行
hset myLock 8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1 1命令,通过这个命令设置一个hash数据结构,在redis中存储的结果为:1
2
3mylock{
"8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1":1
}接着会执行
pexpire myLock 30000命令,设置key的过期时间为30s。
锁存在的时候加锁
如果上一步中客户端1加锁成功了,这时客户端2又来加锁,同样执行这段lua脚本时,第一个if判断语句执行exists发现锁对应的key已经存在,然后会进入第二个if判断语句。在第二个if语句中,执行hexists命令看myLock锁key的hash数据结构中,是否包含客户端2的ID,因为当前数据结构中只有客户端1的ID,所以不存在。最终会执行pttl命令,返回当前key的过期时间。
然后客户端2会进入一个while循环,不停的尝试加锁。watch dog自动延期机制
客户端1加锁的锁key默认生存时间才30秒,如果超过了30秒,客户端1还想一直持有这把锁,怎么办呢?
解决方法其实很简单!只要客户端1一旦加锁成功,就会启动一个watch dog看门狗,这是一个后台线程,会每隔10秒检查一下,如果客户端1还持有锁key,那么就会不断的延长锁key的生存时间。可重入加锁机制
那如果客户端1都已经持有了这把锁了,在线程中又再次加锁会怎么样呢?这设计到可重入锁的概念。
加锁方法还是执行上面那段lua脚本,首先第一个if判断肯定不成立,“exists myLock”会显示锁key已经存在了。然后第二个if判断是成立的,因为myLock的hash数据结构中有客户端1的ID,也就是8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1,此时就会执行重入加锁的逻辑,执行命令1
incrby myLock 8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c71a6b4586:1 1
通过这个命令,对客户端1的加锁次数增1。myLock这个key对应的数据结构变成如下:
1
2
3mylock{
"8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1":2
}也即是,myLock这个key在redis中的hash数据结构中,hash key对应客户端ID,hash value对应加锁的次数。
释放锁机制
如果执行lock.unlock()方法,就可以释放redisson的分布式锁,其释放锁的实现机制也是执行一段lua脚本,源码中的脚本内容如下: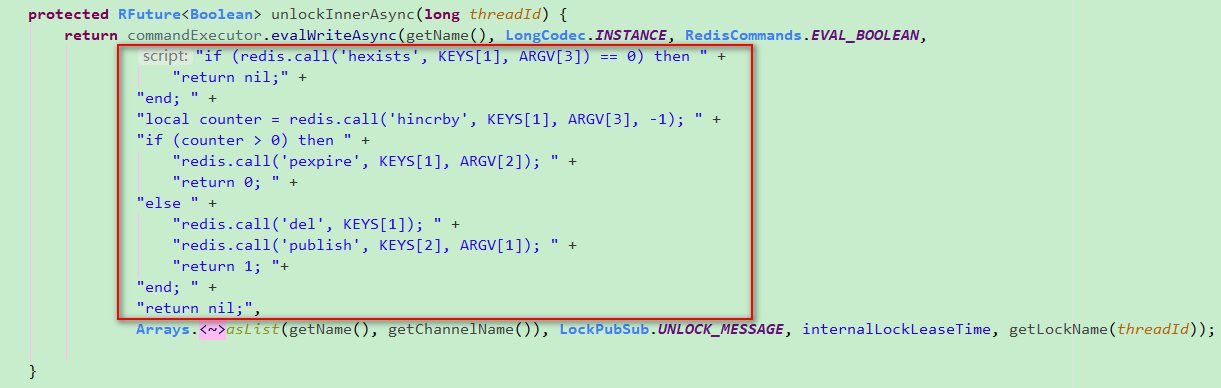
简而言之,就是每调用一次这个方法都对myLock数据结构中的那个加锁次数减1。如果发现加锁次数是0了,说明这个客户端已经不再持有锁了,此时就会用del myLock命令,从redis里删除这个key。至此,锁被成功释放。